Mars Rover Successfully Produces Oxygen
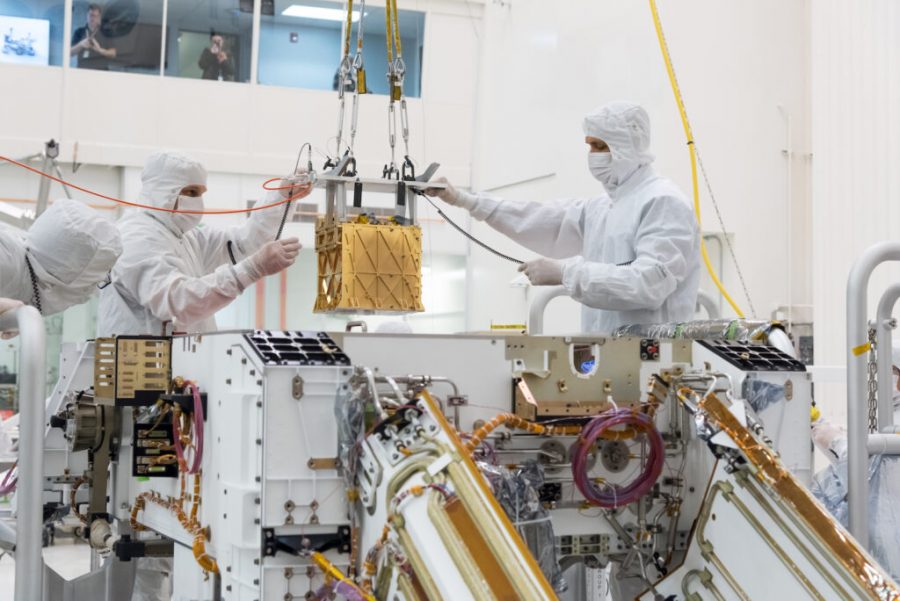
M2020 ATLO – MOXIE Installation Requesters: David Gruel Photographer: R. Lannom Date: 20-MAR-19 Photolab order: 070915-171696
April 23, 2021
On Tuesday April 20th, the Perseverance Rover successfully converted carbon dioxide from Mars’ atmosphere into Oxygen.
This was made possible by the MOXIE instrument attached to the rover. MOXIE stands for Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment. The instrument prepared for two hours and then was able to produce oxygen.
Mars’ atmosphere consists of 96% carbon dioxide and MOXIE was able to produce 5.4 grams of oxygen, which can provide enough air for a person to breathe for ten minutes.
This kind of revolutionary technology has many uses on Earth as well as Mars.
MOXIE’s technology could potentially be used to benefit those on life support and to store oxygen for fuel. However, for the space explorers who plan to visit Mars, MOXIE will be incredibly beneficial in transporting oxygen.
This process would be expensive and lengthy, but with the addition of MOXIE to the project, oxygen would not need to be transported and would simply be produced on Mars.
The discoveries made by the Perseverance Rover and MOXIE are a step further towards Mars exploration.
“I think that’s really cool and that it brings us one step closer to understanding Mars’ environment,” said Gabriela Danger, a junior at ILS.
“This shows how science is always improving and hopefully it will help humans to be able to live on mars in the future,” said Katrina Diaz-Balart, a junior at ILS.